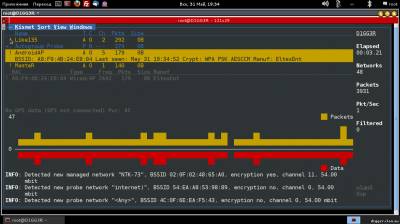
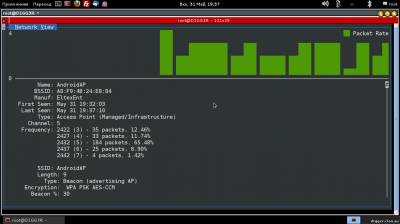
Kismet is a network analyzer for wireless networking of 802.11 b. It allows you to listen to the traffic using almost any supported wireless network adapters using the drivers Airo, HostAP, Wlan - NG, and Orinoco. It is mostly familiar to articles on the topic of hacking, where the program is used to detect hidden networks or packet capture. To hack someone else's network is bad, and yet Kismet is much more than a skeleton key in the hands of the attacker. In an engineer's Arsenal of information security, this software is a great tool for observation and analysis of the ether 802.11. Start Kismet project takes in the distant 2001. Initially released under the GNU GPL and updated regularly for nearly 10 years, the program has managed to grow its community and to enter the top ten network analyzers. Despite the fact that Kismet is a cross-platform development, some features are only available in Linux, and the developer claims in this case about the most complete support. When you run the client you will be prompted to start the server or enter its address. This article assumes that the program is used on a single machine, so you should start local. Depending on the tasks can be passed to the server startup parameters to enable or disable logging, as well as to observe the server console directly in the client interface. After connecting to the server and run the scan will begin. Kismet will display information about the found networks. By default, red is used a network with insecure WEP encryption, green network without encryption, and yellow with WPA. The figures under the list is a visual representation of the data packets and passing in the ether, similar graphs are found in other Windows programs. When you select any network in line, you will see additional information: identifier (BSSID), the time of detection, encryption method, number of packets and amount of data transferred after the discovery. Exclamation mark, dot or space before the name of the network represent three levels of activity, column T — network type (A = Access point), C is the encryption type (W = WEP, N = none, etc). Data fields can be removed, as well as add new ones via the settings menu. On the right shows the total statistics and the Filtered value shows the number of packets that have fallen under the filters. At the bottom is the log, the attentive reader might have noticed there is a connection error with GPSD server. Kismet can work with a GPS device and to provide the captured data to geographic coordinates. If you select a network window opens, which displays more detailed information. You can add two more graphical indicator: signal strength and the number of repetitions through the View menu. The command View → Clients will display a list of clients connected to the selected access point. Here, besides the basic information, added an important parameter: the IP address of the client. Latest Kismet window displays information about the client.
The use of the program in practice
Conventionally, the tasks solved with the help of Kismet can be divided into two areas: analysis and protection. In the first case, the accumulated data must be processed by third-party applications, and in the second Kismet works as a detector of various kinds of network attacks. To consider both profiles are better with specific examples.
Gathering geographical statistics
Most recently, the scandal died down because of the collection by Google of information about Wi-Fi access points and capture the traffic. Indeed, according to Raphael Laterite (Raphael Leiteritz), brand Manager for Google Street View cars collected the coordinates of Wi-Fi access points and GSM base stations for the development of the service navigation and a whole list of good deeds. Worked their system: the Google Street View car used Maxrad antenna BMMG24005 for receiving 802.11 ether and travelled on the route, taking around all the data in the range of Wi-Fi. The obtained data were processed Kismet, which is in communication with a GPS receiver allows you to build high quality station interception.
Create your own Street View car, which will deal with the so-called wardriving not as difficult as it seems at first glance. Additional equipment would need only a GPS receiver to bind data to a geographic location. To begin collecting information, the GPS device must be connected and configured to work through the GPSD daemon. It should be noted that Kismet works with JSON format and therefore be used to test the emulators GPS will not work, unless the supplied GPSD utility gpsfake, which may lose existing logs navigators. However, the GPS settings is beyond the scope of discussion Kismet.
This time the server must be running in logging mode to start collecting information. By default, there are 5 types of logs: alarm Protocol, geographical XML-log, text-based list of detected networks, network XML log and dump the packets in Pcap format. It is because of the latest Google has been prosecuted by the public, as theoretically in this file could be personal data, flying in the air. If done correctly, it is now in the main window will display information on the current geographical position. Contrary to popular belief, Kismet does not know the coordinates of Wi-Fi access point and the geographic data is nothing more than the coordinates of the GPS receiver. Although if you have a large amount of information tracked point is quite real, the program does not attempt such a task is the business of third-party products.
In the process of moving the logs will grow quickly, so you should think about free space available. Data collected from the program is saved in a simple understandable format. For example, we are interested, geographical XML log consists of a set of elements:
<gps-point bssid="00:0C:42:2C:DA:C6" source="00:0C:42:2C:DA:C6" time-sec="1280155487" time-usec="724329" lat="47.133453" lon="28.504967" spd="0.000000" heading="0.200000" fix="3" alt="1225.000000" signal_dbm="-61" noise_dbm="0"/>
All attributes are intuitive and understand the data will not be difficult for any programmer. How to use the data — solution developer. You can build a map of Wi-Fi hotspots in your area, you can develop a system of direction finding. Google announced the collection of these data for the pseudo-GPS navigation when reference not used satellites and base stations. Combining data from different logs you can collect statistics, analyze, draw maps and charts — everything is limited only by imagination. Anyone can build in your car portion of Google Street View and do some useful research activities.
Intrusion detection
The Kismet is more serious, though less popular functionality. It is no secret that many businesses use Wi-Fi for internal communication. Information in such networks is often not intended for the General public. Wireless security air — not less important measure than any other, aimed at the maintenance of internal security. Kismet can detect a large list of network attacks at data link and network layer. For this application, the mechanism of the alarm notifications or simply put — alerts.
Foul trouble for the particular case specified in the configuration file. Consider the work of intrusion detection system on the example of the rules APSPOOF. This is perhaps one of the simplest methods is that it allows one to recognize an attack in which the attacker acts as a fake access point.
The configuration of this rule looks like this:
apsproof=Rule1:ssid="Politia", validmacs="70:3A:02:01:CE:AF"
Validmacs — valid values for the MAC addresses for the access point with the name "Politia", which must be protected. Provoked with Karma attack Tools, Kismet detects instantly what and reports in the Alerts window and the log.
Similarly configured and anxiety. Use Kismet for wireless network security is no more difficult than to capture packets, and in conjunction with other measures, the overall level of security is increased considerably.
Conclusion
Actually about this little program can talk further. The article does not address the topic of plug-ins, greatly expanding its capabilities. Not so long ago Kismet switched to a new kernel, so the number of plugins is not large, but among them there is a decent copy — DECT Sniffer that allows you to use Kismet to work with telephony networks, there is a plugin for Bluetooth
|